The EFQM Model: Concept & Structure
The strategic nature of the EFQM Model, combined with its focus on operational performance and a results orientation, makes it the ideal framework for testing the coherence and alignment of an organisation’s ambitions for the future, referenced against its current ways of working and its responses to challenges |
and pain-points.
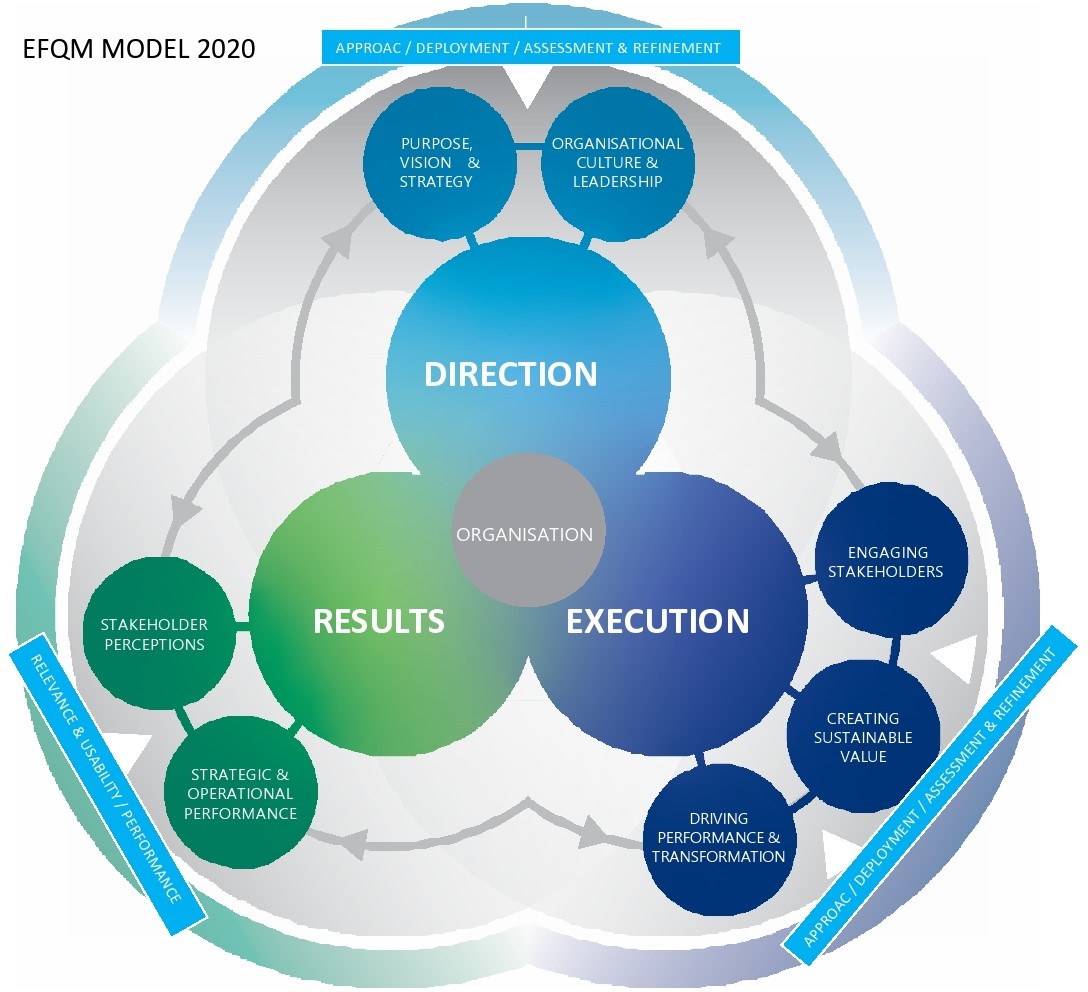
The EFQM Model structure is based on the simple but powerful logic of asking three questions:
- Why does this organisation exist? What Purpose does it fulfil? Why this particular Strategy? (Direction)
- How does it intend to deliver on its Purpose and its Strategy? (Execution)
- What has it actually achieved to date? What does it intend to achieve tomorrow? (Results)
|
|
DIRECTION
This Direction setting prepares the way forward for the organisation to be seen as a leader in its ecosystem and well positioned to execute its plans for the future. |
Positioning statement
For an organisation to achieve and sustain outstanding results that meet or exceed the expectations of its stakeholders it:
- Defines an inspiring Purpose
- Creates a Vision that is aspirational
- Developes a Strategy that is centred on Creating Sustainable Value
- Builds a winning culture
|
Criterion 1
Purpose, Vision and Strategy
Positioning statement
An outstanding organisation is defined by a Purpose that inspires, a Vision that is aspirational and a Strategy that delivers |
The Purpose of the organisation- Explains why its work is important
- Sets the scene for it to create and deliver
- Provides a framework in which it takes responsibility for its contribution to, and impact on, the ecosystem in which it operates.
The Vision of the organisation- Describes what the organisation is attempting to achieve in the long-term
- Is intended to serve as a clear guide
- Provides, along with the organisational Purpose, the basis for setting the Strategy
The Strategy of the organisation:- Describes how it intends to fulfil its Purpose
- Details its plans to achieve the strategic priorities and move closer to its Vision
- 1.1Define Purpose & Vision
Understand: Importance & relevance.
Define: Inspiring Purpose - Appealing to stakeholders
Use: Purpose for creating a Aspirational Vision
Involve: Stakeholders- Connect & Involvement
Identify: Areas for Sustainable & Outstanding results
- 1.2Identify & Understand Stakeholders Needs
Identify S/H and prioritize Key stakeholders- Help / Hinder
Understands how its P and V affects its Key stakeholders
Identify: Key S/H needs & Expectations based on its Purpose & Vision ( P and V)
Analyses factors influencing behavior, relationship and decision making of Key
S/H and the impact on it
Studies and understands Key S/ H Competence and Impact on its PVS
& Business model
- 1.3Understand the Ecosystem, own Capabilities & Major Challenges
Research & Understand: Ecosystem, Megatrends, Link to UNSD goals
& Global compact
Analyses: Different Scenarios for response and impact on its PVS
Knows the potential of its current capabilities to impact its PVS
Investigates and understands Current and future market place
dynamics for the impact on PVS
Assess & evaluate Data, info & knowledge across ecosystem for today
and future
- 1.4Develop Strategy
Develop strategy and related priorities with an action plan and pace aligned to
eco system
Translate Strategy and related priorities into performance targets and
transformation initiatives
Involvement of Key S/H to enable engagement, deployment and
communication- Strategy
Develop Business models that fit the PVS.
Update, Adapt… strategic priorities to based on learning from all sources
- 1.5Design & Implement a Governance & Performance Management System
Design & implement a governance & PMS Aligned to aspirations,
addressing strategy, ecosystem development & challenges.
Puts in place a Governance structure to enable Key S/H Contribution
Defines & implements a Review schedule to monitor progress
incorporating agility that monitors strategy implementation,
Performance & Transformation priorities.
Ensures Perf & Transformation management and reporting is built
in to ensure S/H: Accountability and Transparency.
Makes sure that all legal and regulatory requirements
|
DIRECTION continued
Criterion 2
Organisational Culture & Leadership
Positioning statement
Organisational Culture is the specific collection of values & norms that are shared by people and groups within an organisation that influence,
over time, the way they behave with each other and with Key Stakeholders outside the organisation.
Organisational leadership relates to the organisation as a whole rather than any individual or team that provides direction from the top. It is about the organisation acting as a leader within its ecosystem, recognised by others as a role model, rather than from the traditional perspective of a top team managing the organisation.
|
In an outstanding organisation, leadership is positioned as an activity not a role and leadership behaviours are evident across all levels and parts of the organisation. This role model leadership behaviour inspires others, reinforces, and when necessary,
adapts the values and norms, helping to steer Organisational Culture.
An organisation that aspires to be recognised as outstanding, a leader within its ecosystem, achieves success through a focus on the following activities:
- 2.1 Steer the Organisational Culture & Nurture Values
Understands and steers Culture for alignment to purpose and adaptation if
needed
Nurtures values, Walk the talk- demonstrates desired behaviors of values,
Demonstrates desired behaviors and make people demonstrate the same in their
actions
Expresses and promotes concern- Scarcity of resources, Responsible
Environmental behaviour
Aligns Appraisals, R & R to its values to steer culture
Identifies , recognizes and promotes role models in its ecosystem
- 2.2 Create the Conditions for Realising Change
Works with Key stakeholders for a “ Successful Change”.
Create a Culture of “ No fear for failure”, Fail fast, fail safe approach for learning
Facilitate spirit of learning ,Encourage Improvements & at times transformation,
Determine & demonstrate pace of change, link needs, benefits and
consequences on it PVS
Learns from change management experiences
- 2.3 Enable Creativity & Innovation
Understands importance and benefits of Creativity, Innovation & Disruptive
thinking (CIDt)
Sets ambitious Goals and targets that encourage CIDt
Enables a culture where CIDt is encouraged, learning is encouraged from failures
Develops a culture for expertise for using improvement tools and techniques
Engages with Learning & collaborative networks to identify opportunities for CIDt
Seeks External benchmarking opportunities to keep pace with contemporary environment
- 2.4 Unite Behind & Engage in Purpose, Vision & Strategy
Invests in PVS Communication to S/H to create trust, confidence and
commitment
Encourages & appreciates feedback and concerns on its PVS
Conveys to Key S/Hs their Impact , contribution, Alignment & engagement- PVS
Ensures that key S/H know the importance of alignment to the PVS.
Recognize, Celebrate and share success with key stakeholders to reinforce
desired behavior
|
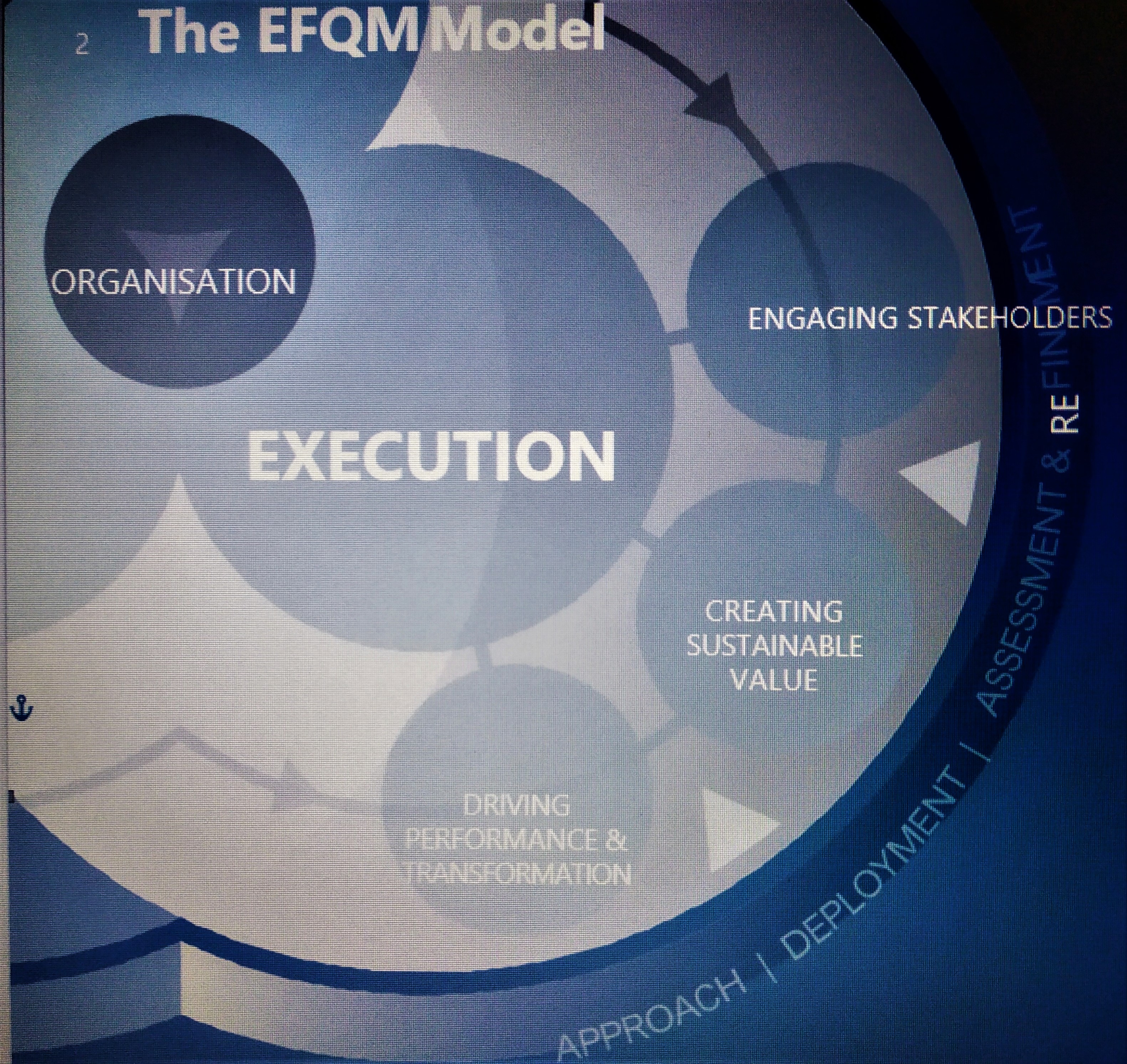
EXECUTION
Positioning statement
For an organisation to achieve and sustain outstanding results that meet or exceed the expectations of its Stakeholders it is necessary, but not sufficient, for it to- Define an inspiring Purpose
- Create a Vision that is aspirational
- Develop a Strategy that is centred on Creating Sustainable Value
- Build a winning culture
The Direction setting as outlined above, prepares the way forward for the organisation, but it then needs to execute its Strategy effectively and efficiently, ensuring that it:
- Knows who the stakeholders are in its ecosystem and engages fully with those that are Key to its success
- Creates Sustainable Value
- Drives the levels of performance necessary for success today and, at the same time, drives the necessary improvement and transformation if it is to be successful in the future.
|  |
Criterion 3
Positioning statement
Having decided which Stakeholders are the most important to the organisation, i.e. its Key Stakeholders, and independent of the specific groups identified, it is highly likely that there is a degree of similarity in applying the following principles when
engaging with Key Stakeholders. |
An outstanding organisation:
- Identifies the specific types and categories within each of its Key Stakeholder Groups
- Uses its understanding of Key Stakeholders needs and expectations to achieve continued engagement
- Involves Key Stakeholders in deploying its Strategy and Creating Sustainable Value and recognises the contributions they make
- Builds, maintains and further develops the relationship with Key Stakeholders based on transparency, accountability, ethical behaviour and trust
- Works with its Key Stakeholders to develop a common understanding and focus on how, through co-development, it can contribute to, and draw inspiration from, the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and Global Compact ambitions
- Actively gathers the perceptions of its Key Stakeholders rather than waiting for them to make contact.
- Evaluates its performance in relation to Key Stakeholders needs and decides on the appropriate actions to be taken to help secure its future, as perceived by these Key Stakeholders.
In practice, we find that an outstanding organisation will include the following groups in the classification of its Key Stakeholders:
- 3.1 Customers: Build Sustainable Relationships
Customers Include Direct, Indirect, users, touchpoints at different stages, prosumers and influencers who are recipients of Products / services and solutions
Identify & classify customers based on defined criteria
Maintain relationship at all stages… including no tangible interaction phase
Understand the communication & Contact needs
Establish: Easy to use communication channels- Agility
- 3.2 People: Attract, Engage, Develop & Retain
People: Individuals / Groups of people engaged by the Organisation
Develop a people strategy aligned to Organisational strategy and plans
Adapts: Needs & expectations- Current and future on all parameters
Enables: People based on PVS for change and developmental needs
Empowers: Communication, sharing, experiences with the ecosystem
Creates: Ambience to thrive with well being supported
Ensures: Proactively guided, rewarded, recognized and cared for
- 3.3 Business & Governing Stakeholders – Secure & Sustain Ongoing Support
Individuals / groups to whom Organization is accountable for its fiscal, legal, ethical and general stewardship requirements. Biz: Owners, shareholders, Investors, Funding Organisations Governing: Govt, statutory & regulatory, Public authority etc
Identifies its Key Business & Governing stakeholders, understands their expectations,
Involves them in transformation ambitions and strategic direction
Forge Mutually beneficial relationships
Makes itself transparent and accountable establishing trust with this group
- 3.4 Society: Contribute to Development, Well-Being & Prosperity
Individuals / Organisations outside the Organisation
Immediate community / Wider society
Uses PVS to develop an understanding of its contribution to the society,
Establishes Develops and maintains relationship with key societal S/HMutual benefit
Utilizes: Easy to use communication channels for Experience sharing- Agile feedback
Makes itself transparent and accountable establishing trust with this group.
- 3.5 Partners & Suppliers: Build Relationships & Ensure Support for Creating Sustainable Value
External parties that the Organization chooses to work with to fulfil its purpose, achieve its vision, deliver the strategy and reach shared objectives
that benefit both parties
Segments: Key partners and suppliers aligned to PVS
Ensures: Alignment of them to Organisation strategy
Build: Trusting relationship for creating Sustainable value
Works: Proactively to leverage culture and expertise for mutual benefit
|
Criterion 4
Creating Sustainable Value
Positioning statement
An outstanding organisation recognises that Creating Sustainable Value is vital for its long-term success and financial strength. |
The clearly defined Purpose of the organisation, enriched by the Strategy, defines for whom the organisation should be customers, segmented appropriately, are the target group for Creating Sustainable Value, although some organisations might also focus on selected Key Stakeholders within its Society or Business & Governing Stakeholder segments.
An outstanding organisation acknowledges that Key Stakeholder needs may change over time and that it is important to collect and analyse feedback to improve or change their products, services or solutions.
The different elements to Creating Sustainable Value are shown below in a step by sequence. It is recognised that the organisational plans for today and the future may well run in parallel or overlap at times, depending on the nature of the organisational business.
- 4.1Design the Value & How it is Created
Understands its differentiators w.r.t competition and uses it for value
creation.
Involves Key stakeholders in co creation for value generation
Develops: Product/ service/ solution portfolio to meet current and future needs for existing and potential target groups aligned to purpose
Designs value considering Life cycle management approaches
Uses qualitative and quantitative methods (data, survey, research) to
improve value proposition & value creation
- 4.2Communicate & Sell the Value
Expresses differentiators and value proposition into engaging
messages for all customer and target groups
Leverages power of networking. Responsible on and off line
behaviour
Uses strategies and approaches to communicate value proposition of
its PSS
Makes it easy for target groups to work with at all stages of the Business.
- 4.3Deliver the Value
Implements effective and efficient ways to create value to deliver its
purpose & value proposition.
Delivers sustainable value through its PSS by meeting / exceeding N & E.
Delivers its PSS minimizing negative social and Env impact
Advises its target groups on responsible use of its PSS
- 4.4Define & Implement the Overall Experience
Uses insights for defining and implementing the overall experience
• Puts in place a consistent, seamless and effective progression with all
touch points during value creation.
Takes advantage to design personalised experiences for target
groups as well as it PSS
Makes sure that people have resources, competence and empowerment to maximise the experience.
Makes sure that people have resources, competence and empowerment to maximise the experience.
|
Criterion 5
Driving Performance & Transformation
Positioning statement
Now and in the future, an organisation needs to be able to meet the following two important requirements at the same time to become and remain successful. |
On the one side, it needs to continue managing successfully the delivery of its current business operations.[Driving Performance]
On the other side, there are constant changes inside and outside the organisation that need to be managed in parallel if it is to remain successful. (Driving Transformation)
The combination of Driving Performance & Transformation confirms the necessity for the organisation to deliver for today while
preparing for the future.
Major elements in enabling performance & transformation are innovation and technology, the ever-increasing importance of data, information & knowledge and the focussed use of critical assets and resources
- 5.1Drive Performance & Manage Risk
Uses: Performance Mgmt System: Link between PVS & Results
Uses PMS: Informed, effective and responsive fact based improvements
Manages: Projects & Improves Process
Identifies: Risks and potential impact on strategic Priorities
Develops: Plans to manage & mitigate strategic, functional & cultural
risks
- 5.2Transform the Organisation for the Future
Identify: Transformation & Change needs aligned to Purpose, Strategy, CSV, Results
Adapts: Strategy and Biz models for today & tomorrow
Build: Organisation structure to deliver PVS,
Establish & Utilize: Agile working approaches- stability for today
Restructures: Value creation Processes based on needs.
- 5.3Drive Innovation & Utilise Technology
Leverages: Innovations for today and the future
Evaluates: Technology for Value creation & Improvements for agility
Introduces:: Relevant developments in Tech for maximizing benefit
Evaluates & manages: Application of Circular economy principles
Provides: Capabilities, resources and tools to develop and sustain
CIDt
Leverages: Innovations for today and the future
Evaluates: Technology for Value creation & Improvements for agility
Introduces:: Relevant developments in Tech for maximizing benefit
Evaluates & manages: Application of Circular economy principles
- 5.4Leverage Data, Information & Knowledge
Ensure: It identifies data to support transformation plans and manage
products
Uses: Advanced Analytics to extract value from data for insights and action
Converts: Data to Info to Knowledge for creating Sustainable value
Makes use : Knowledge from S/H ecosystem for CSV
Ensure: Ethical use of data, info & Knowledge
Secures, Protects and maximizes Knowledge and IP
- 5.5Manage Assets & Resources
Use financial resources in a balanced way for current success and future investment
Responsible use of critical assets, resources, tangible and intangible assets vital for strategy, performance & transformation
Discovers ways to Maximize the value of its assets and resources to suit short & long term Organization & Market demands.
Manage obsolescence, disposal considering circular economy principles
|
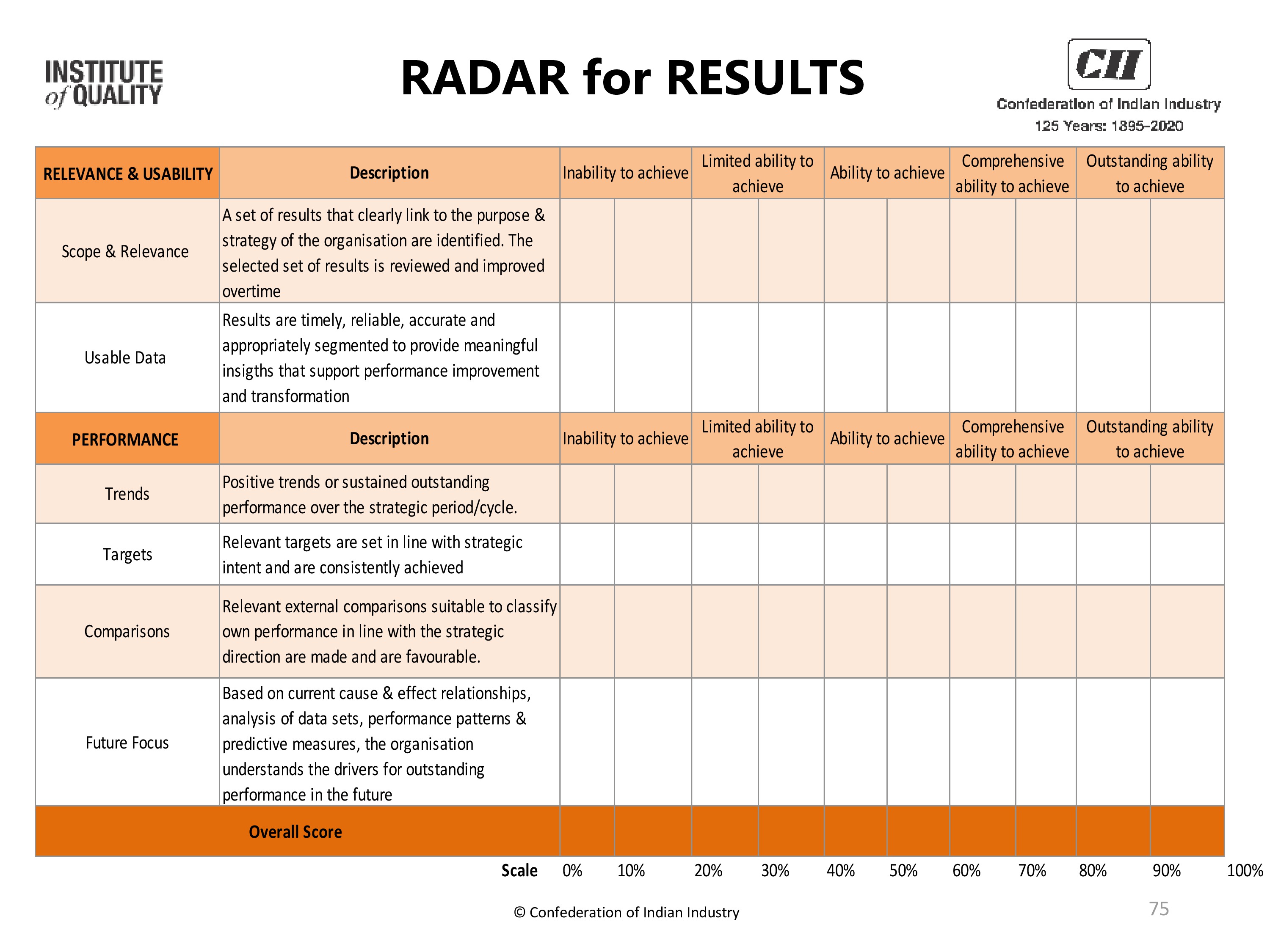
RESULTS
Positioning statement
What the organisation has achieved in relation to what has been described in the Direction & Execution sections, including the forecast for the future. In practice we find that an outstanding organisation provides results data for:
- Stakeholder Perceptions
- Creating Sustainable Value
- Driving Performance & Transformation
|
 |
Criterion 6
Positioning statement
This criterion concentrates on results based on feedback from Key Stakeholders about their personal experiences of dealing with the organisation – their perceptions.
These perceptions could relate to past as well as current Key Stakeholders and could be obtained from a number of sources, including
social media, external recognition, advocacy, structured review meetings, investor reports and compliments/complaints, including feedback compiled by customer relationship management teams.
| In addition to the perceptions that a Key Stakeholder may have of an organisation based on personal experiences, perceptions may also be shaped by the environmental and social impact reputation of the organisation. For instance, the degree to which the organisation is perceived by its Key Stakeholders as contributing successfully
to one or more of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
and Global Compact ambitions.
In practice, we find that an outstanding organisation:- Knows how successful it is at executing its Strategy to meet the needs and expectations of its Key Stakeholders
- Uses its analysis of past and current performance to predict future performance
- Uses Key Stakeholder Perception Results to stay informed and influence its current Direction and the Execution of its Strategy.
Examples of Key Stakeholder Perception Results and topics to be covered could include, but are not listed in any priority order or limited to:
- Customer Perception Results
- People Perception Results
- Business & Governing Stakeholders Perception Results
- Society Perception Results
- Partners & Suppliers Perception Results
|
Criterion 7
Positioning statement
This criterion concentrates on results linked to the organisation’s performance in terms of:- The ability to fulfil its Purpose, deliver the Strategy and Create Sustainable Value
- Its fitness for the future.
These results are used by the organisation to monitor, understand and improve its overall performance and to forecast the impact this performance will have on both theperceptions of its Key Stakeholders as well as its future strategic ambitions.
| In practice, we find that an outstanding organisation:- Uses both financial and non-financial indicators to help it measure its strategic and operational performance
- Understands the linkages between Key Stakeholder perceptions and actual performance and is able to predict, with a high degree of certainty, how future performance will evolve
- Considers the current and future needs and expectations of its Key Stakeholders when deciding on the most appropriate performance indicators to match its strategic & operational objectives
- Understands the cause and effect relationships that impact on performance and uses the results achieved to stay informed and influence its current Direction & Execution
- Uses the results currently being achieved to forecast its future performance with an expected degree of certainty.
Strategic and Operational Performance indicators, could include, but are not limited to:- Achievements in delivering its Purpose and Creating Sustainable Value
- Financial Performance
- Fulfilment of Key Stakeholders Expectations
- Achievement of Strategic Objectives
- Achievements in Driving Performance
- Achievements in Driving Transformation
- Predictive Measures for the Future.
|
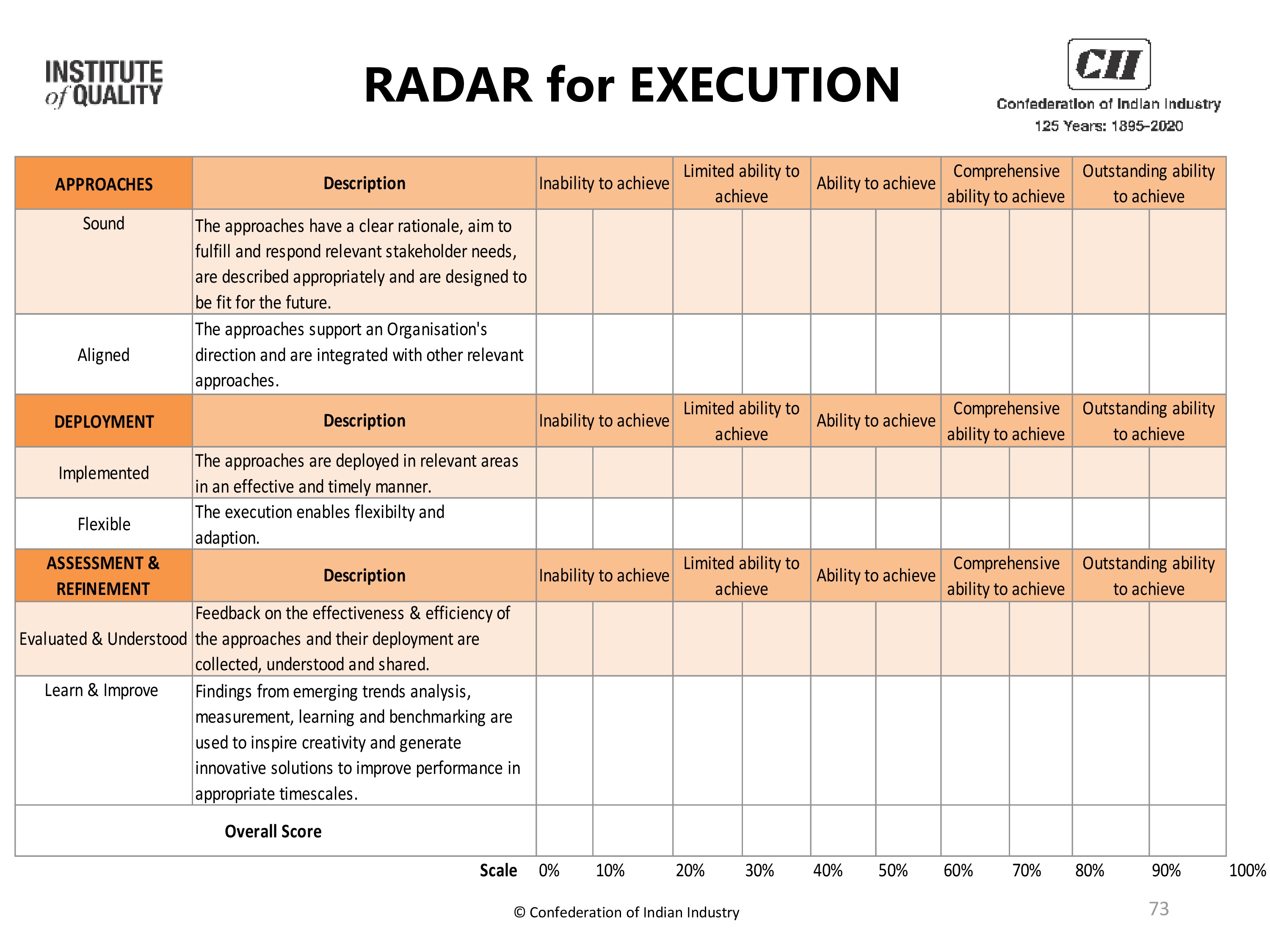
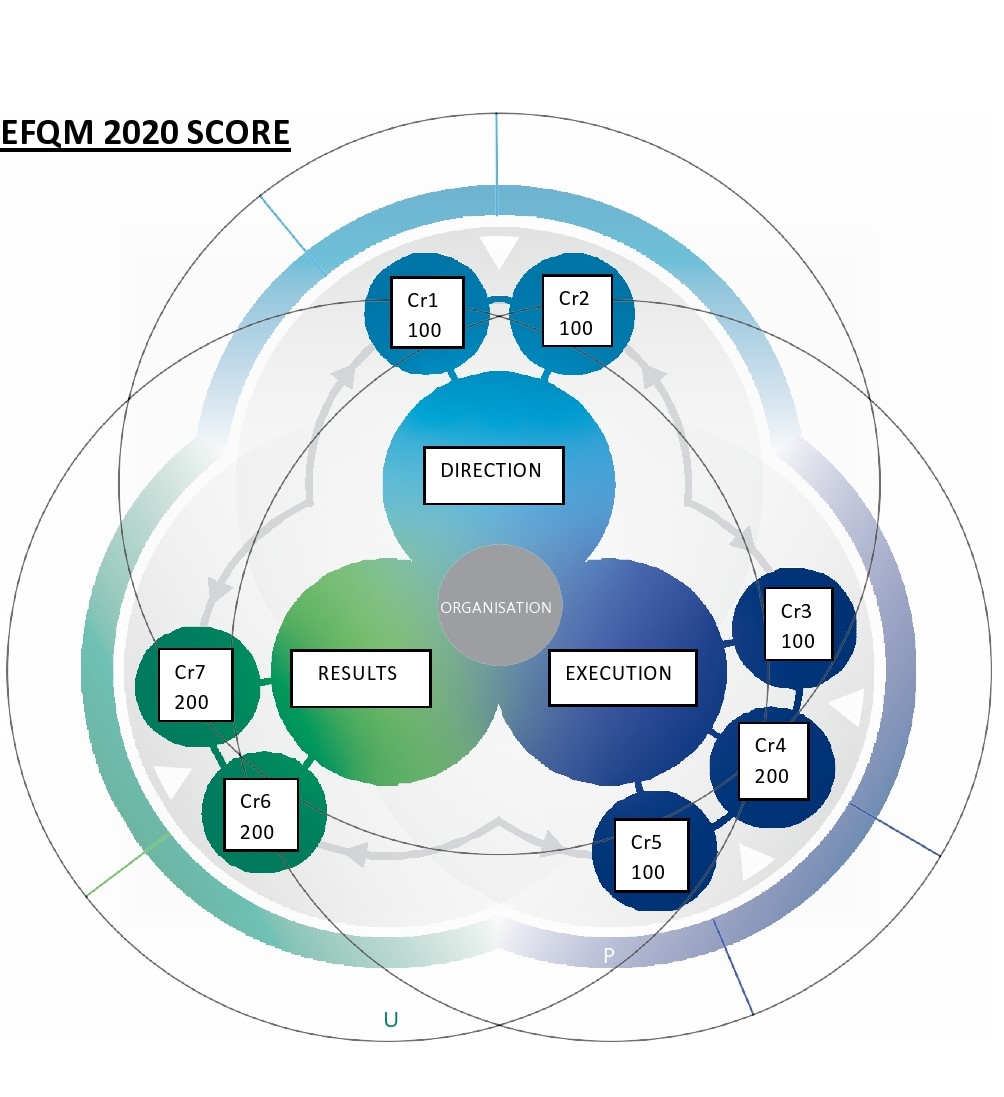
Scoring using the RADAR Matrix Charts
Organisations applying for recognition when assessed against the EFQM Model are scored out of 1000 points. The 1000 points are divided across the seven criteria
as illustrated in the graphic next. |
 |